The gas costs in an apartment or in a private house-building are calculated to determine the costs of heating, water heating and cooking. The calculation is made at the design stage or before the purchase of boiler equipment. The average and maximum gas flow in these cases is calculated according to a certain method, the result gives an idea of the amount of fuel consumed.
Impact on gas consumption
Gas consumption depends on various factors. In large houses, boilers are installed that consume more fuel mixture than units in small buildings or apartments.
Fuel consumption is affected by:
- boiler power;
- outdoor temperature;
- quality of the gas mixture.
Some gas distribution companies supply untreated gas mixtures to the pipeline that contain moisture and impurities. Calorie content decreases and the consumed volume increases.
Gas flow calculation
The power of the boiler or convector depends on the heat loss in the building. The average calculation is based on the total area of the house.
When calculating the gas flow rate, the heating standards per square meter with a ceiling height of up to 3 m are taken into account:
- in the southern regions, 80 W / m² is taken;
- in the north - up to 200 W / m².
The formulas take into account the total cubic capacity of individual rooms and rooms in the building. For the heating of each 1 m³ of total volume, 30–40 W is allocated, depending on the area.
By boiler power
The calculation is based on the power and heating area. The average consumption rate is used - 1 kW per 10 m². It should be clarified that it is not the electric power of the boiler that is taken, but the thermal power of the equipment. Often such concepts are replaced, and the wrong calculation of gas consumption in a private house is obtained.
The volume of natural gas is measured in m³ / h, and liquefied gas in kg / h. Practice shows that 0.112 m³ / h of the main fuel mixture is consumed to obtain 1 kW of thermal power.
By quadrature
The specific heat consumption is calculated according to the presented formula if the difference between the outdoor and indoor temperatures is approximately 40 ° C.
The ratio is used V = Q / (gK / 100)where:
- V - volume of natural gas fuel, m³;
- Q - thermal power of the equipment, kW;
- g - the lowest calorie content of gas, usually equal to 9.2 kW / m³;
- K - the efficiency of the installation.
Depending on pressure
The volume of gas passing through the pipeline is measured by a counter, and the flow rate is calculated as the difference between the readings at the beginning and end of the path. The measurement depends on the pressure threshold in the tapering nozzle.
Rotary counting devices are used to measure pressure greater than 0.1 MPa, and the difference between street and internal temperature is 50 ° C. The rate of gas fuel consumption is read under normal environmental conditions. In industry, proportional conditions are considered to be a pressure of 10 - 320 Pa, a temperature difference of 20 ° C and a relative air humidity of 0. Fuel consumption is expressed in m³ / h.
Diameter calculation
The gas velocity in the high pressure gas pipeline depends on the cross-sectional area of the collector and averages 2 - 25 m / s.
Bandwidth is found by the formula: Q = 0.67 · D² · pwhere:
- Q - gas consumption;
- D - conditional bore diameter of the gas pipeline;
- p - working pressure in the gas pipe or an indicator of the absolute pressure of the mixture.
The value of the indicator is affected by the outdoor temperature, heating of the mixture, overpressure, atmospheric characteristics and humidity. Calculation of the diameter of the pipeline is done when designing the system.
Including heat loss
To calculate the consumption of the gas mixture, you need to know the heat loss of the structure.
Formula used Q = F (T1 - T2) (1 + Σb) n / Rwhere:
- Q - heat loss;
- F - the area of the insulation layer;
- T1 - outdoor temperature;
- T2 - internal temperature;
- Σb - the amount of additional heat loss;
- n - the location coefficient of the protective layer (in special tables);
- R - resistance to heat transfer (calculated in a specific case).
The determination of heat loss is a complex calculation and is carried out by specialists at the project stage. You can order the location of losses at any stage of the operation of the building.
By counter and without
The device determines the gas consumption per month. The standard mixture flow rates are applied if a meter is not installed. For each region of the country, the standards are set separately, but on average they are taken at the rate of 9 - 13 m³ per month per person.
The indicator is set by local authorities and depends on climatic conditions. The calculation is carried out taking into account the number of owners of the premises and people actually living in the indicated housing area.
Calculation of the flow of liquefied gas
Calculation of gas using propane or butane has its own characteristics, but does not present any particular difficulties. The density of the combustible substance, which varies with increasing or decreasing temperature, and depends on the composition of the gas mixture, matters. Only the weight of the liquefied fuel remains constant.
The volume of gas used differs in winter and summer, so it makes no sense to use m³ units to determine the flow of liquefied gas per 1 kW of heat, kilograms are taken for designation, which do not change when the seasons change.
Calculation per 1 kW of heat
The amount is calculated for heating the house and heating the water in the system. If food is being cooked on gas, this must be taken into account additionally.
Formula used Q = (169.95 / 12.88) Fwhere:
- Q - mass of fuel;
- 169,95 - annual amount of kW for heating 1 m² of a house;
- 12,88 - calorific value of propane;
- F - quadrature of the structure.
The resulting value is multiplied by the cost of 1 kg of liquefied mixture in order to calculate the cost of purchasing the required quantity. The price is usually given for 1 kg, and not for 1 m³, which should be taken into account.
How much heat does liquefied gas and natural
 The composition of the natural type of fuel (methane) is determined by its occurrence in the ground. The heat of combustion of a substance is from 7 thousand 600 to 8 thousand 500 kcal / m³, i.e., this amount of heat gives off when burning 1 m³ of gas.
The composition of the natural type of fuel (methane) is determined by its occurrence in the ground. The heat of combustion of a substance is from 7 thousand 600 to 8 thousand 500 kcal / m³, i.e., this amount of heat gives off when burning 1 m³ of gas.
A mixture of butane and propane is used as condensed fuel. A similar indicator of the substance is 9 thousand 500 kcal / m³. The vapor phase of the mixture (combustible suspension in m³) is considered during the evaporation of liquid liters (in kilograms or liters).
Reduced gas consumption
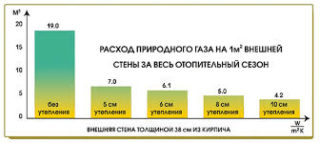
Gas savings are directly related to reduced heat loss. Building envelopes, such as walls, ceiling, floor in the house must be protected from the effects of cold air or soil. Automatic adjustment of the heating equipment is used for effective interaction of the external climate and the intensity of the gas boiler.
Warming of walls, roofs, ceilings
The outer heat-shielding layer creates a barrier to cooling surfaces in order to consume the least amount of fuel.
Statistics show that part of the heated air leaves through the structure:
- roof - 35 - 45%;
- non-insulated window openings - 10 - 30%;
- thin walls - 25 - 45%;
- entrance doors - 5 - 15%.
Floors are protected by a material that has acceptable moisture permeability at the rate, sincewhen wet, the thermal insulation characteristics are lost. It is better to insulate the walls outside, the ceiling is insulated from the attic.
Window replacement
Modern metal-plastic frames with two- and three-circuit double-glazed windows do not allow air flow and prevent drafts. This leads to a reduction in losses through cracks that were in old wooden frames. For ventilation, swing-out mechanisms of the valves are provided, contributing to the economical consumption of internal heat.
Glasses in constructions are glued with a special energy-saving film, which passes ultraviolet and infrared rays inside, but prevents their reverse penetration. Glass is equipped with a network of elements that heat the area for thawing snow and ice. Existing frame designs are additionally insulated with plastic film from the outside or blackout curtains are used.
other methods
It is advantageous to use modern gas-fired condensing boilers and install an automated coordination system. Thermal heads are installed on all radiators, and a water arrow is mounted on the unit's piping, which saves 15 - 20% of heat.
In the heating system, detectors, temperature controllers are installed, which regulate the power of the boiler depending on the state of the external climate. If the weather is warm outside, it’s more efficient and economical to switch to air conditioning heating.