Among the lighting elements, a halogen lamp occupies a confident position. It is almost an analogue of a standard incandescent bulb. It has a number of advantages in comparison with its ancestor.
Definition and device
A halogen lamp is almost the same incandescent bulb, only halogen pairs (iodine or bromine) are added to its bulb. They are also called buffer gases. Thanks to this, it is possible to increase the luminescence of the element up to 3,000 Kelvin and extend the service life. A halogen can work an average of 2,000-4,000 hours. Under the condition of smooth inclusion, the service life can be extended up to 8 000-12 000 hours.
Like a standard incandescent lamp, the lighting element has a cap and bulb.
Principle of operation
Halogen lamps for home or street lighting work like this:
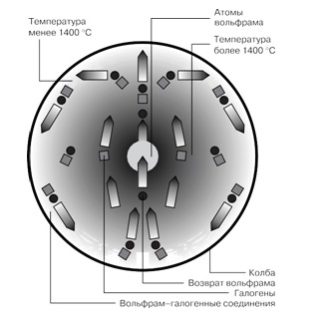
- Electric current flows through the spiral (tungsten glow body), which heats it to high temperatures.
- When heated, the body begins to glow. This is the working position of the bulb.
- Due to the high temperature, the atoms of the tungsten filament begin to evaporate. But they react with bromine or iodine and do not settle on the glass flasks, as is the case with ordinary incandescent lamps, but return back to the spiral.
- This extends the life of the element and enhances its glow.
Halogen bulbs work equally efficiently with direct and alternating currents.
Advantages and disadvantages
Metal halide lamp has several advantages and disadvantages. The pluses include:
- wide scope of application;
- compact bulb;
- ease of installation;
- reasonable market price;
- service life, 2-3 times the operation of a standard incandescent lamp;
- bright glow even with modest parameters;
- Ra level (color rendering) is equal to 99-100, which allows not distorting the colors of furniture, interior items in the room.
Of the minuses, there are such moments:
- the level of efficiency is not higher than 15%;
- working life depends on smoothness and frequency of inclusion;
- the need to install switches with dimmers, which entails additional costs.
If we are talking about a large number of halogen bulbs used, the costs are justified.
Areas of use
MGL is widely used to organize lighting at such objects:
- internal premises for any purpose;
- street lighting lines (lampposts, floodlights);
- car lights;
- aircraft lighting;
- commercial retail premises (window dressing for jewelry, antiques);
- public places;
- lighting devices during photo and video shooting (searchlights, projectors);
- as infrared radiation sources in microwave ovens, soldering irons, electric stoves, etc.
The most beneficial halogen shade all the colors of the cold range.
Varieties of household halogen lamps
There are several types of lighting elements on the market. Each of them has its own technical parameters and characteristics.
Linear
This is the oldest type of halogen. Externally, it is a tube with two R7s sockets at its ends. Halogen linear lamp requires mandatory horizontal placement. The power range of such elements is 1-20 kW, depending on the size.Most often used for projector lighting. The length of the tube can vary from 78 to 118 mm.
With external flask
Identical in structure and construction with conventional incandescent lamps. They also have a flask, inside which is another quartz, and Edison's base (E14 or E27). These halogens can be used even without lights.
The glass of such a light bulb can be milky, transparent or dull. There are also elements in which the material of the bulb absorbs UV radiation.
The flask can have a different shape - polygonal, hexagonal, candle-shaped, pear-shaped, etc.
Elements with an external bulb are not needed for the transformer, and a protection block for smooth switching would be desirable.
With reflector
These halogen lamps for a 220 volt home are produced in three standard sizes - MR8, MR11 and MR16. The luminous flux of the elements is characterized by different angles of incidence.
Halogen device: bulb with integrated reflector. There are metal reflectors (aluminum) that direct the beam of light forward. There are also interference reflectors that divert the light back. This increases the temperature of the filament, which leads to a brighter glow and lower heat loss. Thus, economical energy consumption occurs.
Reflector bulbs are best used for spot, directional lighting. It is advisable to connect them through a transformer.
Capsule
These elements are tiny in size and equipped with a G9 cap. Decoding of the marking means that the distance between the pins here is 9 mm. Therefore, they are also called g9 halogen lamps. In capsule lamps, the glow body can be longitudinal or transverse. The main purpose of such elements is to operate in lamps and chandeliers without upper decorative glasses. G9 halogen lamp can also be used in built-in furniture lighting.
Low voltage systems
For these types of lamps, xenon was used as filling gas. Luminous flux increased by 10% with the consumption of the same power as other halogens. Low voltage elements are ignited instantly. The main areas of application are medical optics or special lighting devices.
Protection block
To further strengthen the period of operation of the halogen, the masters use a protection unit. The main task of the device is to provide a smooth current supply to the bulb when it is turned on. Often with a sharp admission, the element simply burns out.
As a result, the current supply, and hence the brightness intensity, gradually increase within 1-2 seconds. The protection unit has two outputs. The phase-ground, input-output and polarity are of no fundamental importance.
Often the unit is called a soft starter.
Halogen lamp transformer
All halogens are divided by the class of operating voltage - 220 volts and 12 volts. When replacing halogen lamps with g4 12v LED lamps, a transformer is required. It also protects the lighting elements from power surges and overheating.
There are two types of transformers:
- Toroidal. It is considered the simplest. It is assembled from a core and two windings. The main advantages are excellent reliability, easy connection, low price.
- Pulse (electronic). In its design, such a transformer has a core, two windings and a magnetic circuit. There are four types of electronic devices, depending on the shape of the core and the location of the windings on it - armored, toroidal, rod and armored. In addition, pulse transformers differ in the number of turns of the windings. The main advantages of electronic transformers are compactness, low weight, a large input voltage range, the absence of noise and heating during operation.
- Impulse
- Toroidal
Pulse transformer has a high efficiency.
Halogen and LED lamp comparison
Many craftsmen are wondering which lamps are better - halogen or LED for the home. It is important to consider the features of the technical parameters of both types of lighting devices:
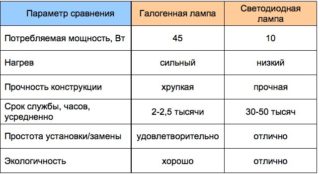
- The level of energy consumption of an LED is less than that of a halogen. Both lamps are more profitable than standard, with a tungsten filament.
- Power. 60 W halogens correspond to the power of a 100-Watt conventional lamp. The same level of power gives a 10 W LED.
- Lifetime. LED lamp - 100,000 hours. Halogen - about 4,000 hours
- Both types of elements reach maximum brightness in 1-3 seconds.
- Glow spectrum. Halogens - cool white. LEDs - neutral, warm and cold to choose from. In addition, Led bulbs can have different colors.
- Disposal LEDs are in household trash. Halogens - require special disposal, as they can pollute the environment.
- Permissible operating temperature range. LEDs - from -90 to +200 degrees. Halogen - from -130 to +160 degrees. Thus, the latter cannot be used where there is poor heat dissipation: in cramped rooms, in furniture, in fixtures with tightly closed shades.
- Price. LEDs are five times more expensive than metal halide.
It is possible to put Led lamps instead of halogens, but only if the network works perfectly without voltage surges. At the same time, the cost of purchasing LEDs will pay off over time due to more economical energy consumption.
Based on the knowledge of the listed parameters and the difference between the two types of lamps, the master can choose the type of element for the specific conditions of their use.
Operational Features
Proper operation of halogen lamps implies:
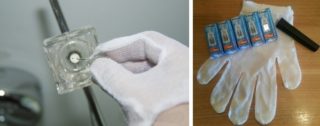
- Mounting elements with gloves or through a clean, dry cloth. This is due to the fact that grease stains and prints remain on the glass flask. Later, due to the high temperature of the heated lamp, black spots form on its body. This is the burned fat of the left imprint. Such marks lead to overheating inside the bulb and its further failure.
- It is important to avoid touching the bulb of the mounted bulb with any materials. Especially with wood, fabric, paper, and other flammable ones.
- Do not touch the working halogen with your hand. Severe burn possible.
If the element is used with a dimmer, you need to periodically light the lamp for 10 minutes at full power. From this, the precipitate of tungsten iodide accumulated in the flask will evaporate.
Halogen bulb check
The performance of the element can be checked with a multimeter. He put in the mode of determining the minimum resistance. Next, operate according to the scheme:
- take the lamp by the bulb with a dry cloth;
- A probe inserted into the VΩmA connector leads to the base terminal.
If the element is operational, the multimeter will show resistance ranging from 0.5 ohms to several units. If the result on the device screen is closer to infinity, then the halogen is inoperative.