Energy saving is the most important task for any owner of a house or apartment. In order to save, there is a transition to energy-saving lamps, which include fluorescent lamps. Luminescent light sources are actively used both in residential buildings and for lighting office buildings or storage rooms. Before purchasing a device, you need to understand what advantage fluorescent lamps have over incandescent lamps, what technical characteristics they have and what types of devices are.
The device of a fluorescent lamp and principle of operation
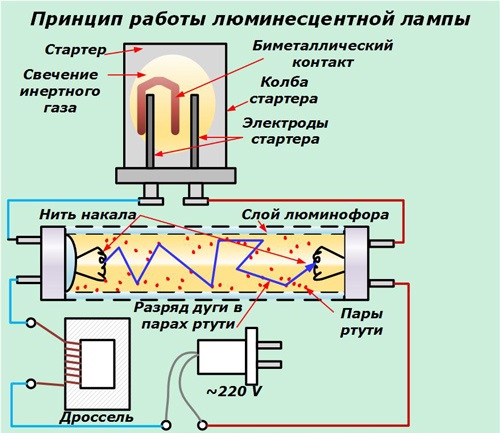
A fluorescent lamp is a device that is used to create lighting. The lamp has a number of structural similarities with classic incandescent lamps or halogen devices. To understand what a fluorescent lamp is, you need to understand its structure. The luminescent device consists of a sealed bulb and electrodes. In a durable glass flask is a mixture of gases and mercury, the inner part is covered with a phosphor. Along the edges there are electrodes made of tungsten filament, to which the contacts passing current are soldered.
An electric current is supplied, which is supplied to the electrodes. The thread heats up, resulting in a discharge, accompanied by ultraviolet radiation. This glow passes through the walls of the bulb, the phosphor and turns into ordinary visible light.
Due to the presence of mercury and other harmful substances in the composition, the LL lamp must be handled carefully, being careful not to damage it. It must not be disposed of as ordinary household waste - a fluorescent light bulb, like a halogen one, is handed over to a special collection point.
Light source specifications
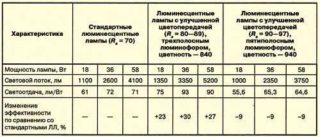
Fluorescent lamps have not only technical characteristics. Like any electrical product, they have electrical characteristics, and like a lighting fixture, they have light parameters.
Electrical specifications include:
- Rated voltage. Mains voltage that is suitable for lamp operation. It is 220 V or 110 V.
- Working voltage. The value on the lamp when it burns. It is equal to half the nominal one and is 100-110 V for a 220 V network and 45-60 V for 110 V.
- Ignition voltage The value on the bulb required for the appearance of a discharge. It is much higher than the network value and is not a constant. Depends on the ignition circuit, environmental conditions.
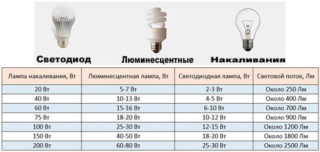
- Rated power. According to this indicator, low-power (up to 18 W), medium power (up to 58 W) and powerful (from 58 W) devices are distinguished. Also on sale you can find high-intensity light bulbs with a power of 150 W, but they are practically not used due to low efficiency.
- Efficiency. Luminescent lighting gives a coefficient of performance greater than 20%.
- The diameter of the flask is 12.16.26.38 mm.
- Base sizes 14 and 27 mm.
Lighting characteristics of discharge lamps:
- Nominal luminous flux. It is set 100 hours after burning.
- Color rendering index. Depends on lamp design. In standard devices it is equal to 50-70%, in lamps with increased color rendition it is 97%.
- Colour temperature. Shows what shade the glow will have. Fluorescent lamps range from 2700 K to 6500 K.
Performance characteristics:
- Luminous efficiency depends on the color and power.The largest household lamps LB 40 W - 80 lm / W. Of the produced lamps, the maximum light output of the T5 series with electronic ballasts is 104 lm / W.
- Average burning time. Depends on the electrodes and the strength of the oxide film covering them. For medium power lamps, the duration is 15,000 hours.
- Ripple coefficient. In most fluorescent lamps, it is 23%, except for devices with improved color rendering, in which a value of 70% is reached.
- Depends on the ambient temperature. At low temperatures, ignition conditions deteriorate. The operating temperature range is from 5 to 55 ° C.
- Disposal Since the lamp contains mercury and other harmful components, it must be disposed of in a special way. To do this, the device must be taken and taken to a special collection point.
In terms of their characteristics, luminescent light sources are significantly superior to classic bulbs.
The main types of fluorescent lamps
Luminescent light sources can be divided into the following groups:
- Linear Are applied to illumination of offices, warehouses, productions, sports grounds. They have increased power and light output. Save about 30% of electricity.
- Compact. Also called household energy-saving. They look like ordinary bulbs. Used for general purposes in classic lighting fixtures. Also found their application in the illumination of advertising display cases, hospital rooms. They have a long service life and high light output.
Also, lamps can be divided as follows:
- Standard. The inside of the flask is coated with one layer of phosphor. Used in home lights, desktop lighting devices.
- With increased light transmission. They have a three-layer or five-layer phosphor.
- Special. Various components may be added to the phosphor. They are used in show business, tanning salons, and bactericidal lamps.
The most common types are high and low pressure gas discharge mercury lamps. High-pressure devices are used in street lighting and high-power luminaires. Low-pressure lamps are used in lighting residential premises and manufacturing enterprises.
The choice of the type of lamp directly depends on the lamp in which it will be used, and on its purpose.
Network connection
Gas discharge lamps cannot be directly connected to the power grid because of the high cold resistance and negative differential resistance.
These problems can be corrected by applying ballasts. The most common are EMPR (electromagnetic ballast) and electronic ballasts (electronic).
EmPRA is an electromagnetic inductor that is connected in series with the lamp. In series with the filament spirals, a starter is connected, which is a neon lamp with bimetallic electrodes and a capacitor. Advantages - simplicity of design, reliability, durability. Disadvantages - a long start-up, a large amount of electricity is required, a hum during operation, flicker, large sizes.
The electronic ballast feeds the bulb with a high-frequency voltage, which prevents flashing. It uses two options for starting lamps:
- Cold. The lamp turns on immediately after applying voltage.
- Hot. The electrodes are heated and the source lights up after 0.5-1 second.
The advantages include a long service life, lower power consumption, the possibility of dimming on some models, and noiselessness.
Labeling LL
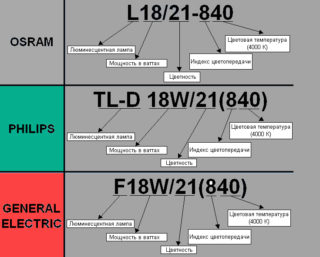
There are two types of marking lamps that differ from each other: domestic and foreign.
The Russian designation consists of a set of letters and numbers. The decryption definition is as follows:
- The first letter A denotes a lamp.
- The second letter indicates the characteristic of the light flux.D - daytime, HB - cold white, TB - warm white, EB - natural, B - white, UV - ultraviolet, C - blue, K - red, H - green, G - blue, F - yellow.
- The third sign is the color rendering quality. C - increased, CC - the best.
- The fourth character designates. A - amalgam, K - circular, P - reflex, B - quick start, U - U-shaped.
- The last digits are the power in watts.
Also on the lamp may be abbreviation LHE or LE. It stands for natural or cold natural light.
Foreign marking consists of a three-digit number and a signature in English like cool white (cold light). Designations can be found in the tables.
Pros and cons of fluorescent tubes
 Luminescent devices rank second in sales after LED devices. This is due to their advantages:
Luminescent devices rank second in sales after LED devices. This is due to their advantages:
- energy saving;
- high quality of light;
- good light output;
- a wide selection of products for general and special purposes;
- Duration of operation - the norm is 10-40 thousand hours;
- when burned out, the bulb is easy to change.
Disadvantages:
- Cost. First of all, you need to calculate what budget will be spent on the installation of fluorescent devices instead of classic light sources. This is quite expensive, but due to the length of the work, the money will quickly pay off.
- Negative effect on human health with prolonged exposure. Harm to the eyes.
- Dependence of service life on the number of on and off cycles.
- High risk of breakage during power surges. Requires the installation of a stabilizer or other device to protect against drops. Otherwise, the device may burn out.
- Incompatibility with dimmer.
- Noisy work. The light bulb can buzz quite loudly, which is why people in the room may feel discomfort.
- Inability to use in dusty and humid rooms. To work outdoors requires a high class of protection against dust and water.
- Danger due to mercury.
- The fragility of the flask.
- The need for heat dissipation.
- Poor performance at low temperatures.
- The choice of the color of the glow of LED lamps is greater than that of the fluorescent backlight.
The product has many drawbacks, but if the operating conditions are observed, the bulb will light up the declared time.
Fields of application
Luminescent light is used almost everywhere. This is the illumination of houses, shop windows, aquariums, non-residential premises, streets. Luminescent and neon lighting is actively used in various performances and concerts. Also, light sources can be used to create plasma screens for televisions and computers.
The main area of application is the illumination of large areas. Stadiums, playgrounds, courtyards are illuminated with fluorescent devices with a dust and moisture protection housing. This is due to the high light output and the minimum number of on and off cycles - it is enough to turn on the lights once a day in the dark.