One of the most important requirements for the regular operation of electrical appliances in residential premises is potential equalization. It is characterized by a decrease in the potential difference between the surface of the floor covering, the ground and the grounded metal parts of electrical appliances. Equalization of potentials is possible by laying on the surface of special conductors that are connected to ground. This circuit is simple but effective because it reduces contact stress in damaged insulation.
Why do you need to equalize the potentials
Before you find out what a PCC in an electrician is, you need to deal with concepts such as electric potential and current. You can get acquainted with their physical properties by the example of an ordinary conductor. When it is at rest, all charged particles are uniformly filled in its internal cavity, they are negative and positive.
If we talk about every object that generates current, then one of its poles is crowded with electrons, and the other is lacking. When a conductor is connected to it, the electrons inside will rotate in the opposite direction until the balance is reached. This movement is called electric current, and the difference in electrons is the negative and positive electric potential.
The current is constant if, with a constant potential difference, the electron motion will be directed in one direction. If the state is characterized by a constant change in the direction of the electrons, the current is called alternating.
The home network is characterized in that such changes occur at intervals of 50 seconds. It follows that the frequency of the alternating current is 50 Hz. The surface of all conductors through which electric current flows must be insulated and located in places where there is no contact with surrounding objects. This applies to all parts made of metal, for example, metal parts and structures that have zero electric potential - no current should flow through them. With proper and correct operation, they perform their tasks autonomously and do not pose a potential threat to the health and life of households.
Reasons and danger
 Before eliminating the potential difference, you need to find out what are the main reasons for its appearance. Provoking factors:
Before eliminating the potential difference, you need to find out what are the main reasons for its appearance. Provoking factors:
- static electricity generation;
- regular exposure to stray currents;
- high atmospheric pressure (such phenomena are often observed when there is a thunderstorm on the street).
- structural changes in metal structures and parts.
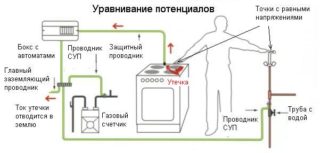
A special danger is the leakage of electric currents from the wires of the wiring, a short circuit on the housings of household appliances and other electrical appliances. Most often, this phenomenon can be found in the bathroom - by touching a wet tap or pipe, you can get an electric shock. This happens most often due to destruction of the insulating layer or violation of the integrity of the wires. This and similar situations can lead to negative consequences, for example:
- A person stands on the floor and at this moment touches the battery or pipe, which, as it turns out later, is under voltage. Each surface that a person touches has a different potential, therefore, the current begins to pass through his body. The result is electrical injuries of varying severity.
- If the floor surface was not insulated, but grounded, a person will inevitably be shocked.
In order to prevent the occurrence of dangerous situations in the future, it is necessary to connect all equipment and devices that should not be energized into a single circuit. In this case, during the development of emergency situations, all surfaces will have the same electric potential.
Types of potential equalization boxes (PMC) and their device
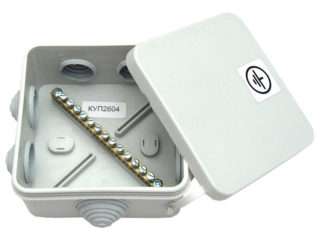
 PMC in electrics is divided into two types:
PMC in electrics is divided into two types:
- Main - OSUP.
- Additional - DSUP.
Each has its own technical features, advantages and disadvantages, so you should familiarize yourself with them in more detail.
Potential control box
This potential equalization box is considered the leading one. It is a contour that combines the following work elements:
- grounding box;
- lightning protection system;
- GZSh - the main grounding bus (it is required to mount it at the input to the structure);
- water pipes made of metal (cold and hot water supply);
- ventilation system box;
- metal parts of the reinforcement of a residential structure.
A few decades ago, the household did not know anything about such a problem as the potential difference. The reason for his appearance was the installation of plastic pipes that conduct electric current, which leads to an open circuit.
DSUP box
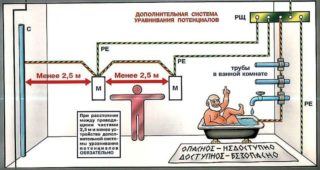 This potential equalization system is considered auxiliary, they are installed in the bathroom. The system includes the following working parts:
This potential equalization system is considered auxiliary, they are installed in the bathroom. The system includes the following working parts:
- ventilation system box;
- shower or bath enclosure;
- sewer system;
- towel dryer;
- heating, water and gas pipes.
Each part of the additional potential equalization system is connected by a separate wire to a core made of copper. Its second end is connected to the DCS.
Principle of operation and installation of PMC
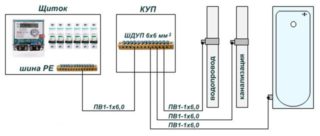
To prevent the formation of a potential difference, a control box is installed in the rooms. The principle of operation of the device is the parallel connection of all structures made of metal. The PMC box combines all conductive objects into a single circuit.
It is not difficult to establish a potential equalization system at home. It is called the local system. It is recommended to install such a structure during repairs in the apartment, since it is required from the distribution panel to the PMC to conduct a wire under the floors.
To install the installation, the following tools and materials will be required:
- Fixing connections - fixing petals, clamps, bolts. They are used to connect the wires of the entire circuit.
- Terminal box with busbar made of copper (BDUP).
- Single core copper wires. The cross-sectional area of such cables should vary between 2.5 - 6 mm.sq., grade - PV1.
If all the necessary equipment has been prepared, you can proceed with the installation. Preliminary make a diagram of the connections in order to correctly balance the potentials. The cable locations from the box to the ground bus in the switchboard are also schematically shown.
The next stage is preparation for connecting the communications themselves. They clean contact points until a characteristic metallic luster is formed. This is important because it provides a reliable connection. In an emergency, emergency, the potential equalization system will not fail.
Lead the cables to each part of the circuit. All conductors lead into a box and make a reliable connection to the bus.
The terminal box installed in a room with high humidity should have a degree of protection of the enclosure of at least IP54.
The best option is to install the system at the stage of building construction, however, there are restrictions on its use:
- It is forbidden to install in houses where a TN-C type grounding system with a PEN conductor is installed.
- If plastic pipes made of polyethylene are installed at home, they will break the circuit, which will lead to electric shock.
The cross-sectional area of the conductor used must be at least the recommended value.
Lightning protection system in equipotential bonding
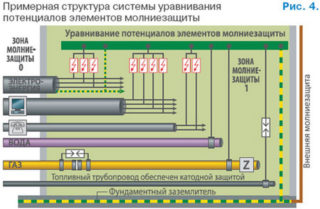 When the building is struck by lightning, a high rate of increase in current strength is observed. Against this background, a significant potential difference is formed.
When the building is struck by lightning, a high rate of increase in current strength is observed. Against this background, a significant potential difference is formed.
In order to prevent uncontrolled power surges and short circuits when struck by lightning, it is necessary to connect all electrical devices, lightning protection, grounding, metal objects with a potential equalization system. All circuit conductors are connected using an equalizing bus. Large building structures are usually equipped with several large tires. Moreover, they must be connected to each other.
The lightning protection potential equalization box should be installed at the entrance to the structure, as well as in places where it is not possible to maintain safe distances, for example, in the basement or at the same level with the ground. In a building made of concrete or with a metal frame, equalization of the system should be carried out exclusively at ground level. In tall buildings, such systems are installed at intervals of 20 meters.