When placing networked lighting fixtures (lamps or LED strips), doubts as to how to connect them together, as a rule, do not arise. If they are designed for a voltage of 220 volts, the traditionally used method of switching on is connection in parallel. Serial connection of bulbs is used only in rare cases when garlands are made on their basis, for example. Another common reason for using this method is the desire to increase the life of lighting products, using them at part-time working power.
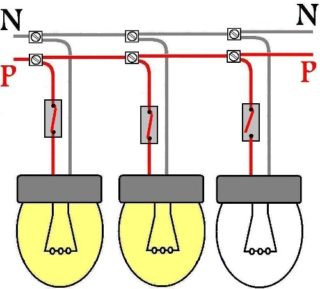
Serial connection
An atypical series connection of bulbs to a 220 Volt network has the following characteristics:
- the same current flows through all the lighting elements included in the circuit;
- the distribution of voltage drops on them will be proportional to the internal resistances;
- accordingly, the power spent on each illuminator is distributed.
When the bulbs are connected in series with a common switch, the 220-volt-rated illuminators will not burn at full strength.
When two incandescent bulbs with different power P are installed in a chain, one of them burns brighter, which has a large resistance, that is, less energy-intensive. The explanation is very simple: because of the greater internal resistance, the voltage on it will be more significant in magnitude. Since this parameter is included in the formula for P squared P = U2 / R - with a fixed resistance, a large power dissipates on it (it burns brighter).
 The advantage of sequentially turning on the lamps is a more gentle operation due to the lower power consumed by each of them. In all other respects, this method of connection is undesirable, since it has the following characteristic disadvantages:
The advantage of sequentially turning on the lamps is a more gentle operation due to the lower power consumed by each of them. In all other respects, this method of connection is undesirable, since it has the following characteristic disadvantages:
- when one lamp fails, the entire circuit is de-energized, so that the lighting line completely stops working;
- when installing bulbs of different power, they give a different glow;
- the inability to use a serial circuit when connecting energy-saving lamps (they need a full voltage of 220 volts).
The serial version is optimal for creating “soft light” in sconces or in the manufacture of garlands of low-voltage LED elements.
Parallel connection
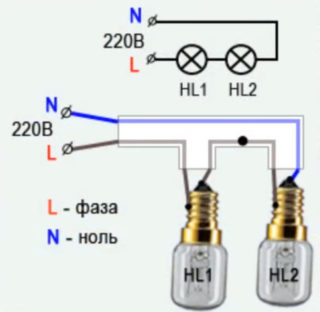
The classic parallel connection of the lamps differs from the serial method in that in this case the full mains voltage is applied to all the illuminators.
When the bulbs are connected in parallel, each of the branches flows its own current, which depends on the resistance of this circuit.
Conductors connected to lamp sockets and lampholders are connected to one wire in the form of a parallel assembly. The indisputable advantages of this method include its following features:
- when one of the bulbs burns out, the rest continue to work;
- in each of the branches they burn at full power, since all are simultaneously applied to full voltage;
- it is allowed to use energy-saving light bulbs;
- To connect to the network, it is enough to remove the required number of phase conductors from the room chandelier and arrange them as a switched group.
There are practically no drawbacks to this method, with the exception of a large consumption of conductors with highly branched chains. Without problems, you can connect several bulbs to one wire by using the principle of wiring.A typical circuit for parallel connection of light bulbs with a switch is no different from ordinary switching. In this case, a key switch is additionally introduced into it.
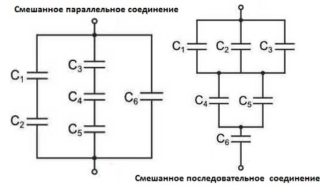
Mixed Compound Laws
The mixed inclusion of illuminators is described as follows:
- It is based on the parallel connection of several electrical branches.
- In some of the branches, the loads are switched on sequentially in the form of a series of light bulbs arranged one after the other.
It is allowed to connect various types of consumers into separate parallel branches, including incandescent lamps, as well as halogen or LED sources.
When considering the characteristics of a mixed compound, the following laws must be taken into account:
- The same current flows through each of the series-connected sections of the circuit.
- When passing through a link with consumers connected in parallel, it forks, and at the output it again becomes single-line.
- With an increase in the number of elements in the working circuit, the absolute value of the current in it decreases.
- The voltage at one link is equal to the product of the current component by the total resistance of the branch (Ohm's law).
- With an increase in the number of elements in the circuit, the voltage at each of them decreases correspondingly.
A mixed connection method has several advantages determined by the merits of each of the two main connection schemes. He “inherited” its profitability from a sequential one, and from a parallel one - the ability to work even if an element fails in one of the combined chains.
When using a mixed circuit, it is recommended to group lamps of the same power into serial circuits, and install illuminators with different power consumption in parallel branches.
Types of lamps and wiring diagrams
Before installing various types of lighting fixtures, it is advisable to familiarize yourself with the principle of operation and their internal structure, as well as with the features of the power circuit. It is also important to know that each of the varieties is able to work for a long time only with strict observance of the operating rules.
Fluorescent lamps
In addition to traditional incandescent lamps, their luminescent tubular analogues are often used to illuminate office and partly domestic spaces. They are most often installed on the following objects:
- in workshops and on conveyor lines of industrial production;
- in office buildings and in various boxes;
- in garages, trading floors and similar public places.
Much less often they are used at home - sometimes put in the kitchen to organize the illumination of the working area.
A feature of fluorescent illuminators is the inability to directly connect to a 220 Volt network, since a high voltage is required for the breakdown of a gas column. To turn them on, a special electronic circuit is used, which includes such starting elements as a throttle, starter and high voltage capacitor (in some cases it is not necessary).
In recent years, uneconomical and very humming during operation choke converters are replaced by the so-called "electronic ballast". The order of its connection is usually indicated in the form of a diagram depicted on the device body.
When using an electronic adapter, one discharge lamp is connected, or two pieces are installed at once, connected in series.
Halogen sources and LED bulbs
The first type of illuminators are traditionally installed during the installation of suspended and suspended ceilings. They are also ideal for lighting areas with high humidity, as they are available in several versions.One of them is designed to work from 12 volts. To obtain them in the area of ceiling ceilings, a converter is installed that is designed for the corresponding output voltage.
LED lamps are characterized by the presence of a built-in driver that allows you to get the right supply voltage (12 or 24 Volts). Samples of LED illuminators, designed for operation from 220 Volts, turn on like incandescent lamps. But unlike conventional illuminators, it is not recommended to include them in a sequential chain.
It is important to choose the right type of lamps to determine the desired order of their connection. It is not allowed to connect energy-saving illuminators in a serial chain, when installing fluorescent and halogen lamps, they are guided by the schemes for their inclusion. With reduced mains voltage, energy-saving lamps quickly fail, and fluorescent lights may not light up at all.