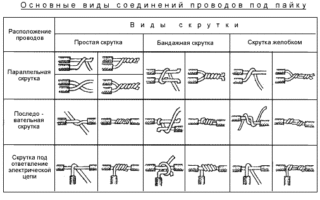
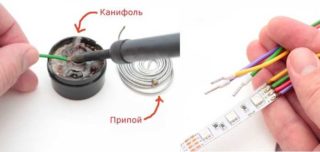
Without exception, all wiring diagrams provide for the branching and connection of cables and wires. This requires an additional installation of a junction box, which is made of metal or polymeric materials. However, it is not enough to establish the design, it is important to know the technology of soldering the twisted wires in the distribution box.
What are junction boxes for?
The need for junction boxes should not be in doubt. To verify this, you should read the warnings of specialists:
- Neglecting the installation of the structure is a violation of the rules set forth in regulatory documents.
- Compliance with fire safety. Thanks to the RC, the probability of short circuits and fire is significantly reduced, this is due to the tightness of the structure.
- Installation of the device will take a lot of time, but in the future it will be much easier to upgrade, maintain, repair and build wires. For example, if you need to install an additional outlet or switch, the necessary wires can be brought out of the junction box.
In general, installation of a junction box is required. The installation technology is simple, complexity can arise when connecting wires.
General Switching Rules
The implementation of the soldering method resembles welding, only an ordinary soldering iron is used, and not an inverter apparatus with electrodes. Before twisting the veins you need to tin. To do this, the soldering iron is heated, immersed in rosin, and held several times until the appearance of a reddish tint on the areas cleaned from insulation.
For quality work, you must first check the soldering iron tip. It is important that it is clean. If the surface is uneven, dirt has accumulated on it, it will be impossible to make high-quality solder. Contaminants are removed with a file, then its end is repeatedly tinned.
The advantages of soldering over other connection methods
There are several ways to connect the wires in the junction box, however, only soldering and welding differ in the minimum transition resistance and monolithic connection. Everyone can solder the wires at home. Welding will require experience and the availability of a special welding machine.
To carry out the work, the following set of tools will be required:
- flux;
- a knife designed to remove insulating material;
- solder;
- side cutters;
- soldering iron;
- pliers or pliers;
- sandpaper.
Having not prepared all the necessary tools and consumables beforehand, it is impossible to start work.
Soldering wires
Tinning and soldering of cables in the junction box is carried out in several stages.
- Removing the insulating layer.
- Wire stripping before the appearance of a characteristic shine of metal.
- Service.
- Twisting.
- Soldering.
- Isolation
Before proceeding with the connection of conductive conductors, it is necessary to analyze what length is required. The wires are cut so that when soldering, the ends are located outside the junction box. At the end of the work, they are laid in any desired way.
Soldering wires in the junction box is not allowed to be tight. The stock in this case is also inappropriate.
To remove the insulating layer, a special tool is used - a stripper or a sharp knife. When working with a sharp knife, the movements should resemble the planing of a pencil. It is forbidden to cut the insulating layer with pliers or side cutters; you cannot make circular cuts. Transverse damage in the near future will cause a break.
For a wire intended for soldering, stripping varies within 1.5-3 cm. The number of turns is at least 2.
The wires before soldering are thoroughly peeled and tinned so that oxides do not appear on the surface of the wires, which impede normal conductivity and increase resistance. Already tinned conductors are twisted using pliers or pliers.
The soldering of twisted copper wires in a box has a similar algorithm. The twist should be tight, but not stretched, otherwise the ends of the conductive wires can simply break off.
Finally, twisted wires are soldered with a soldering iron so that the solder is coated with a uniform layer on all sides. The quality of work depends entirely on how well the ends were cleaned.
Soldering iron power selection
 For high-quality performance of work, it is required to use fairly powerful soldering irons, at least 65 watts. This is especially important when working with copper wires, since copper is a good conductor of heat, therefore, removes heat from the soldering point. If the power of the device is not enough, this can lead to "cold soldering" - the solder does not uniformly cover the soldered area, and the strength will be low.
For high-quality performance of work, it is required to use fairly powerful soldering irons, at least 65 watts. This is especially important when working with copper wires, since copper is a good conductor of heat, therefore, removes heat from the soldering point. If the power of the device is not enough, this can lead to "cold soldering" - the solder does not uniformly cover the soldered area, and the strength will be low.
The device should optimally warm the place for 1 minute or more, the surface of the solder at the end of work should be smooth, have a uniform shine.
Solder type
There is a wide variety of solders, the main ones are listed in the table.
| Solder mark | Structure (%) | Tensile strength (kg / mm) | Melting temperature | Application |
| POS-30 | Lead - 70
Tin - 30 |
3,2 | 266 | For soldering and tinning of parts made of steel, copper and their alloys |
| POS-40 | Lead - 60
Tin - 40 |
3,8 | 238 | For soldering and tinning of contacts and parts in radio equipment made of galvanized steel |
| POS-90 | Lead - 10
Tin - 90 |
4,9 | 220 | For soldering and tinning of medical instruments and metal utensils |
| POS-61M | Copper - 2
Lead - 37 Tin - 61 |
4,5 | 192 | For soldering and tinning of printed conductors and copper wires |
| POS-61 (tertiary) | Lead - 39
Tin - 61 |
4,3 | 190 | For tinning and soldering of live parts made of bronze, brass and copper with tight seams |
| POSV-33 | Bismuth - 33.3
Lead - 33.3 Tin - 33.3 |
– | 130 | For soldering parts made of constantan, brass and copper with a tight seam |
| POSV-50 (Alloy Rose) | Bismuth - 50
Lead - 25 Tin - 50 |
– | 94 | For machining parts that are susceptible to overheating |
| Alloy d Arce | Bismuth - 45.3
Lead - 45.1 Tin - 6.9 |
– | 79 | For the manufacture of fuses, tinning and soldering of parts susceptible to overheating |
| Wood Alloy | Cadmium - 12.5
Bismuth - 50 Lead - 25 Tin - 12.5 |
– | 68,5 | An important feature is toxic. Designed for the manufacture of fuses, tinning and soldering of parts susceptible to thermal effects |
The last three grades have a low melting point and low alloy strength.
Oxidation protection
To protect the soldering place from oxidation by oxygen, a flux is used. When working with copper, the following are most often used:
- Rosin, it contains only pine rosin.
- LTI-120 includes triethanolamine (1-2%), aniline hydrochloride (3-7%), ethyl alcohol (66-73%), rosin (20-25%).
- The composition of alcohol rosin includes ethyl alcohol (60-70%) and rosin (30-40%).
The simplest, cheapest and at the same time common version of the flux is ordinary rosin. The only difficulty that may arise when working with a substance is a solid state of aggregation.
Soldering and Tinning Technology
When starting to solder or tin-wire, it is important to place the wires horizontally so that the soldering iron tip touches all sides without hindrance. Some "experts" recommend placing conductive wires vertically, but this is not worth it, since drops of solder may begin to spread.
Before tinning, the wires are heated with a soldering iron and in parallel they touch the place of heating with a piece of rosin until it begins to melt. If liquid flux is used, it is applied first before heating starts. After tinning, the wires are twisted.
Soldering technology is slightly different, since more solder is required here. A flux is applied to the conductive wires and warmed up with a soldering iron until the molten drop is evenly distributed. If necessary, the procedure can be repeated.
Soldering with a burner and crucible
If there is a large front of work, it is advisable to use crucibles, which are a hollow metal cylinder equipped with a handle for filling with molten solder. This device can be heated using a gas burner or used as a nozzle on a powerful soldering iron.
The capacity contains a small amount of molten solder, while it freezes, a person manages to make several twists.
Precautionary measures
Caution should be exercised during work, as molten solder can leave severe burns if it comes into contact with skin. All brands of solders contain lead, the vapors of which are toxic to humans. To prevent poisoning, you need to work in a respirator.
When soldering wires, it is forbidden to use acid-containing active fluxes, since after completion of work they require complete removal. Flux residues have a destructive effect on all materials, especially soldering acid and zinc chloride are aggressive for copper.
In general, the work should not cause difficulties, the main thing is to familiarize yourself with the execution technology in advance, prepare all the consumables and tools.